1.5 Vulnerability Repository
Vulnerability Repository is a collection of Vulnerability Sources (VulSource).
Vulnerability Repository scans public vulnerability databases periodically and builds Supported Open-Source Projects from source.
The public vulnerability databases are first processed into a baseline Vulnerability structure:
| Field | Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID | string | CNVD/CNNVD/CVE ID | CNVD-2025-03269 |
| Title | string | Short description of the vulnerability | SAP NetWeaver Application Server Java 跨站脚本漏洞 |
| Products | []string | List of products affected by the vulnerability | SAP SAP NetWeaver Application Server Java null |
| RiskLevel | int | Risk level (-1: Unknown, 0: Critical, 1: High, 2: Medium, 3: Low) | 2 |
| CVEID | string | Related CVE ID (if applicable) | CVE-2023-12345 |
| SubmittedDate | string | Date of submission (optional) | 2025-02-19 |
| PublishedDate | string | Date of publication | 2025-02-20 |
| UpdatedDate | string | Date of update (optional) | 2025-02-21 |
| Description | string | Description of the vulnerability (HTML escaped) | SAP NetWeaver Application Server Java... |
| Type | string | Type or category of the vulnerability | 通用型漏洞 |
| Patch | string | Patch information (if applicable) | 目前厂商已发布升级补丁以修复漏洞... |
1.5.1 National Vulnerability Database (NVD)
CVE: Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures is hosted by NIST under NVD - Vulnerabilities.
They are available in the GitHub repo CVEProject/cvelistV5: CVE cache of the official CVE List in CVE JSON 5 format. This repo contains CVE from project start (1999) and updated regularly.
Each CVE consists of its CVE-ID, publish date, description, associate reference links, vulnerable product configuration, CWE weakness categorization, Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) and other metadata.
1.5.1.1 Archival Data
cvelistV5 is cloned and processed to generate VulSource.
1.5.1.2 Live Data
Vulnerability Repository synchronize cvelistV5 with upstream to get the latest CVE listing.
Then the updated CVEs are processed to generate VulSource.
This task is scheduled to run once a week.
1.5.2 China National Vulnerability Repository of Information Security (CNNVD)
There's no consistent method to directly associate open-source projects from CNNVD listing. As most of CNNVD references to CVE, project filter is not applied during scraping and use CNNVD info to enrich the corresponding CVE vulnerability.
1.5.2.1 Archival Data
Archival data is available as daily, monthly or yearly zip from 国家信息安全漏洞库.
This download requires login.
Findings
- all 135302 records have CVE ID
- has 编号撤回 records
- XML don't have 报送时间 (
submitted_date) - XML don't have
patchandproducts - XML don't escape for invalid characters
- severity doesn't match the corresponding CVE
https://gitlab.astricsa.cf/PRP069-24CI/vulnerability_repo/-/tree/main/api-server/cli/import_vul/FINDINGS/severity_compare
1.5.2.2 Live Data
An automated browser is used to visit the public listing at https://www.cnnvd.org.cn/home/loophole and fetch CNNVD vulnerabilities newer than a "CNNVD last fetch date" stored in Vulnerability Repository's database.
This task is scheduled to run once a week.
1.5.3 China National Vulnerability Repository (CNVD)
There's no consistent method to directly associate open-source projects from CNNVD listing. As most of CNNVD references to CVE, we do not apply project filter during scraping and use CNNVD info to enrich the corresponding CVE vulnerability.
1.5.3.1 Archival Data
Archival data is available as weekly XML from 国家信息安全漏洞共享平台. This download requires login and solving captcha.
Findings
- 12727 of 56375 records does not have CVE ID
- XML don't have 更新时间 (
updated_date) - type may be slightly different for HTML and archive XML (e.g. "通用型漏洞" vs "通用软硬件漏洞")
- 75 duplicated CNVD IDs in 2020
https://gitlab.astricsa.cf/PRP069-24CI/vulnerability_repo/-/tree/main/api-server/cli/import_vul/FINDINGS/dup_vulnerabilities - XML don't have patch URL, only state patched
- severity doesn't match the corresponding CVE
https://gitlab.astricsa.cf/PRP069-24CI/vulnerability_repo/-/tree/main/api-server/cli/import_vul/FINDINGS/severity_compare
1.5.3.2 Live Data
The customized browser is used to visit the public listing at https://www.cnvd.org.cn/flaw/list and fetch CNVD vulnerabilities newer than a "CNVD last fetch date" stored in Vulnerability Repository's database.
This task is scheduled to run once a week.
1.5.3.3 Anti-bot measures
The CNVD website employs anti-bot protections, including a script that checks for the presence of webdriver in the window object. To enable automated browsing, we need to customize the browser to remove property.
1.5.4 VulSource
A VulSource for a Supported Open-Source Project consists of:
- corresponding pseudo assembly codes before and after the vulnerability fix
- syntactic features for code blocks related to the vulnerability
- meta-data for reporting:
- path of source code in project tree
- mapping of source code to pseudo assembly code (in line numbers)
for each vulnerability in the CVE.
VulSource's are is deployed manually to SourceGuard, via offline archive or downloading from remote Vulnerability Repository. It can be customized according to license agreement or the use case of the customer.
SourceGuard's /vulsource/ API query the local VulSource snapshot.
1.5.4.1 Vulnerability Source Preparation
- Generate baseline
Vulnerabilitys for NVD. - We use
Productsfield to filter the Supported Open-Source Project. - We developed a Vulnerability Enrichment Tool to scrape GitHub using both GitHub API and web scraping technology to enrich a vulnerability.
- For each Supported Open-Source Project we:
- enrich the vulnerabilities with associate reference links, vulnerable product configuration, affected versions, commit IDs and version to date mappings using Vulnerability Enrichment Tool
- enrich the vulnerabilities with related vulnerabilities in CNNVD and CNVD
- do Vulnerability Feature Extraction (see below) for the vulnerabilities
- add the pseudo assembly code and source code diff to the code blocks relating to the vulnerability fix to this vulnerability
- Expose the database and Vulnerability Features with FastAPI-based web service
Sample of an enriched vulnerability for Linux kernel:
{
"id": "CVE-2022-23222",
"note": "NULL Pointer Dereference",
"poc_collected": true,
"references": {
"Ubuntu": "https://ubuntu.com/security/CVE-2022-23222",
"Debian": "https://security-tracker.debian.org/tracker/CVE-2022-23222",
"SUSE": "https://www.suse.com/security/cve/CVE-2022-23222",
"Red Hat": "",
"ExploitDB": "https://www.exploit-db.com/search?cve=2022-23222",
"NVD": "https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2022-23222"
},
"format": "sourceguard-collected",
"description": "kernel/bpf/verifier.c in the Linux kernel through 5.15.14 allows local users to gain privileges because of the availability of pointer arithmetic via certain *_OR_NULL pointer types.",
"poc_location": "https://github.com/JlSakuya/Linux-Privilege-Escalation-Exploits/tree/main/2022/CVE-2022-23222",
"fix_info": {
"breaks": "",
"guidance": "v5.17",
"message": "",
"fixes": "c25b2ae136039ffa820c26138ed4a5e5f3ab3841"
},
"repositories": [
{
"repo_label": "CNNVD",
"note": "Linux kernel 代码问题漏洞",
"description": "Linux kernel是美国Linux基金会的开源操作系统Linux所使用的内核。 Linux kernel 5.15.14及之前版本存在代码问题漏洞,攻击者可利用该漏洞获得特权。",
"id": "CNNVD-202201-1165"
},
{
"repo_label": "CNVD",
"note": "Linux kernel代码问题漏洞(CNVD-2022-06892)",
"description": "Linux kernel是美国Linux基金会的开源操作系统Linux所使用的内核。\nLinux kernel 5.15.14及之前版本存在安全漏洞,攻击者可利用该漏洞获得特权。",
"id": "CNVD-2022-06892"
},
{
"repo_label": "NVD",
"note": "NULL Pointer Dereference",
"description": "kernel/bpf/verifier.c in the Linux kernel through 5.15.14 allows local users to gain privileges because of the availability of pointer arithmetic via certain *_OR_NULL pointer types.",
"id": "CVE-2022-23222"
}
],
"affected_versions": {
"date_mappings": {
"v5.17-rc1": "2022-01-22T16:00:00Z",
"v2.6.12-rc2": "2005-04-15T16:00:00Z"
},
"last_affected": "[UNKNOWN]",
"from": "v2.6.12-rc2",
"to": "v5.17-rc1"
},
"cvss": {
"risk_level": 1,
"score": 7.800000190734863,
"v2": 7.199999809265137,
"v3": 7.800000190734863
}
}
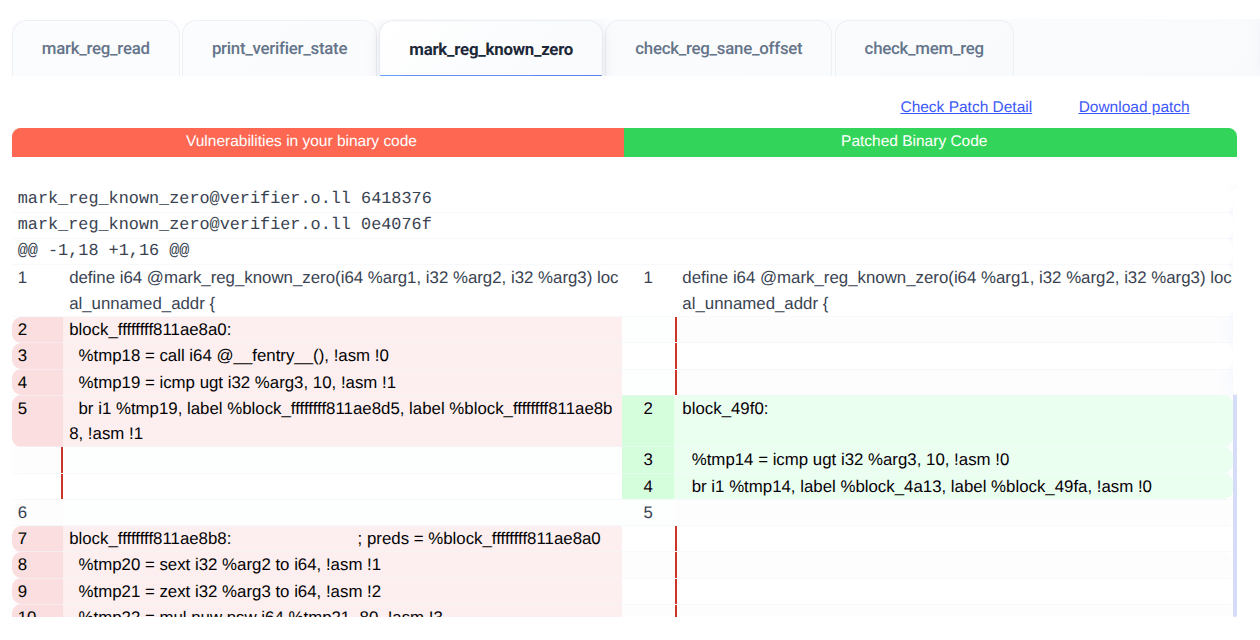
Pseudo assembly code diff for a kernel vulnerability:
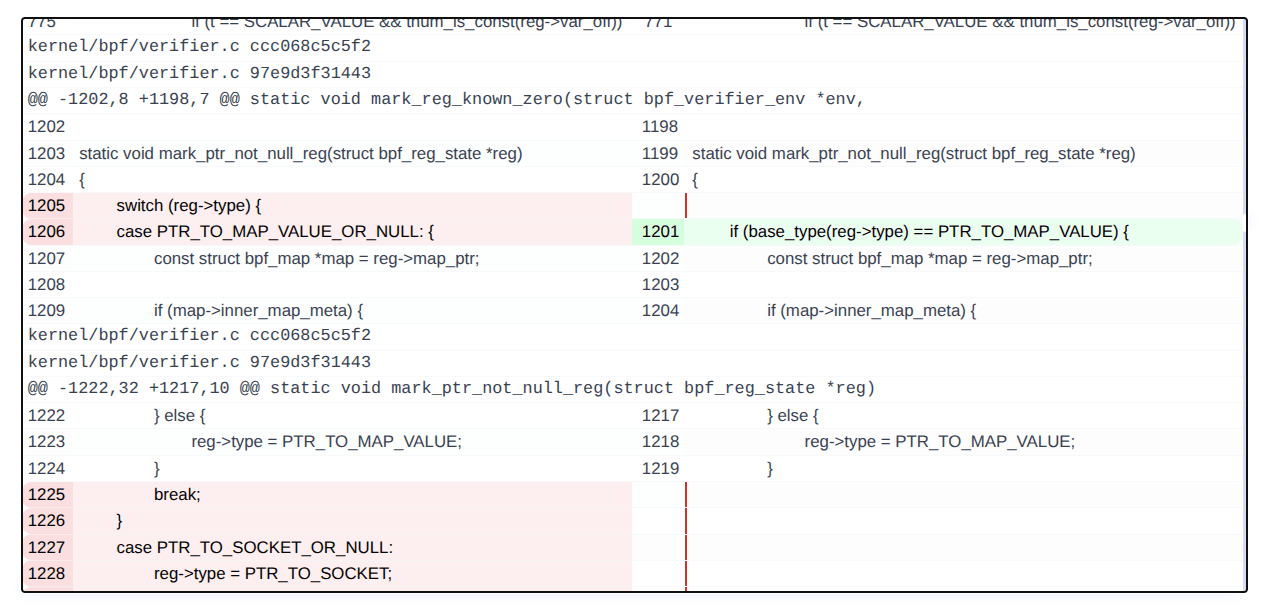
Source code diff for a kernel vulnerability:
1.5.4.2 Vulnerability Feature Extraction
To enhance vulnerability identification, we further process Supported Open-Source Projects listed in CVE records to extract detailed vulnerability features. For each specific vulnerability, the following steps are performed:
1. Source Code Retrieval
- Clone the source code of the relevant open-source project locally.
2. Binary Compilation
-
Build the project's binaries before and after vulnerability fix using commit IDs provided in the patch information.
-
If no fix is available:
- Use the latest commit as the before-fix version.
- Leave the after-fix version empty.
3. Disassembly
- Disassemble the binaries into architecture-independent pseudo assembly code.
- This removes variations caused by different CPU architectures and compiler settings.
4. Syntactic Feature Extraction
For each code block, analyze the pseudo assembly code to extract the following features:
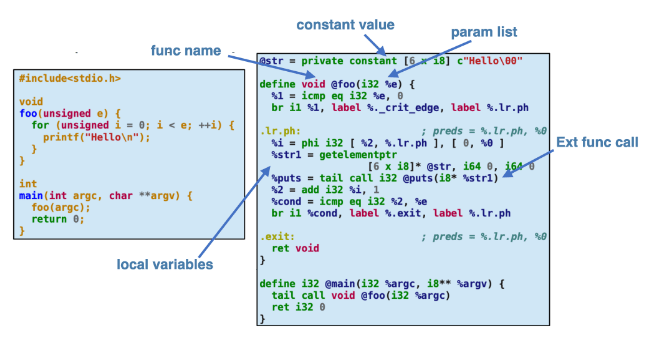
- Unmangled Function Name
Since the binaries are built from source, we can reconstruct the un-mangled function name using its scope and symbol information.
Example:std::ostream& std::operator<< <std::char_traits<char>>(std::ostream&, char const*) - Function Parameter Lists
The type and order of input and output parameters are extracted. - Constant Values
The declaration site and constant names and values are extracted. - Global Variable Usage
The calling site and global variable called are extracted. - External Function Calls
The calling site and the function called are extracted. - Local Variable Count
The calling site and the number of local variables are extracted.
5. Integration with Hybrid Vulnerability Identification Engine
- The extracted syntactic features are used in the Static Analysis phase to quickly identify code blocks related to the vulnerability.
- The pseudo assembly code from both before and after vulnerability fix is also used in the Dynamic Analysis phase to determine if the vulnerability if found in the binary.
For more details, refer to Hybrid Vulnerability Identification Engine.