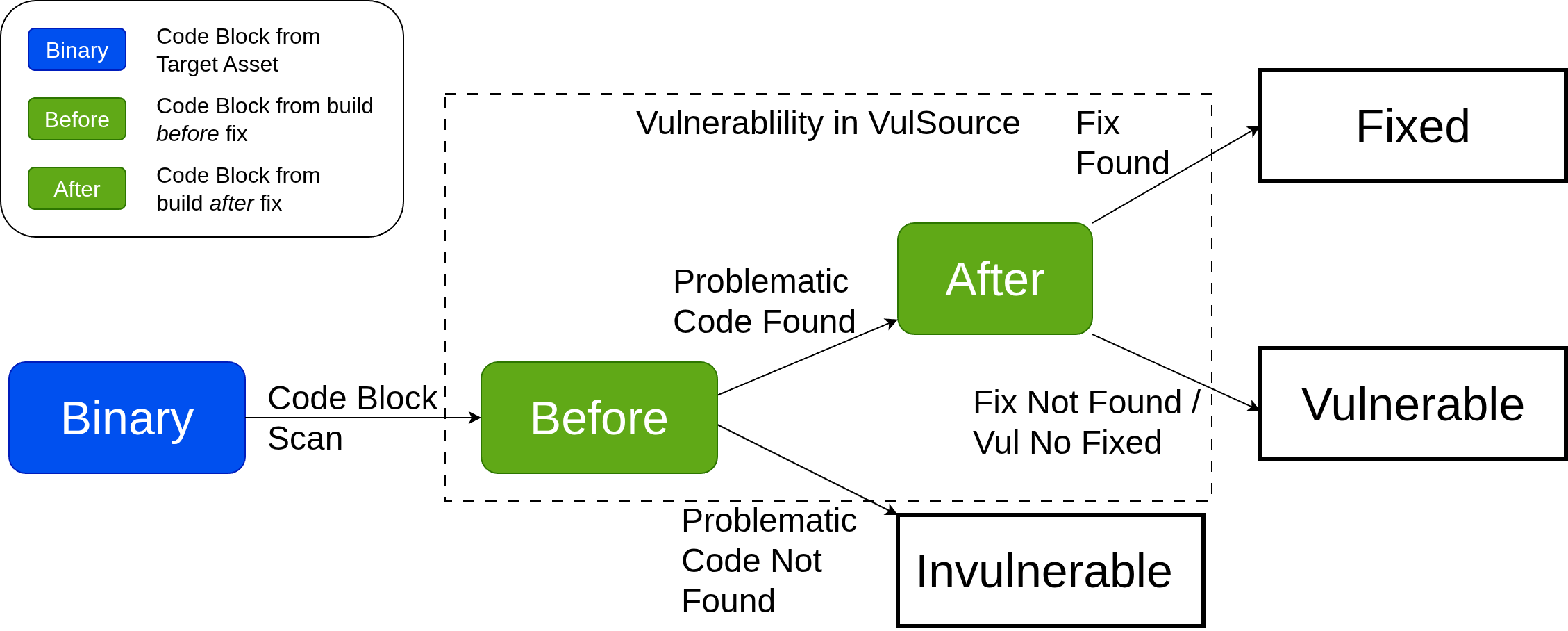
1.6 Vulnerability Scan
Asset (Target Device) Management module will login the Assets with Asset Agent using the credentials provided by the User. Asset Agent will scan for supported binaries in the Assets in predefined paths and upload the binaries to SourceGuard Server. These binaries will then be scanned by Hybrid Vulnerability Identification Engine.
Project Management module will store the scan results and present in Web Frontend.
1.6.1 Hybrid Vulnerability Identification Engine
Given a Target Binary, the Hybrid Vulnerability Identification Engine will perform the following steps:
1. Disassembly
- The binary is disassembled into architecture-independent pseudo assembly code.
- This process eliminates variations caused by different CPU architectures and compiler options.
2. Feature Extraction
For each code block, the engine analyzes the pseudo assembly code to extract syntactic features, including:
- Unmangled Function Name
Compilers often mangle function names during compilation.
For example:std::ostream& std::operator<< <std::char_traits<char>>(std::ostream&, char const*)may be mangled as_ZStlsISt11char_traitsIcEERSt13basic_ostreamIcT_ES5_PKc.
We use existing algorithm (fromllvm-cxxfilt) to recover the original names. - Function Parameter Lists
- Constant Values
- Global Variable Usage
- External Function Calls
- Local Variable Count
This step is similar to the process described in Vulnerability Feature Extraction.
3. Static Analysis
Each code block is compared against known vulnerabilities from VulSource using the extracted syntactic features.
-
Matching is performed in a prioritized order:
- Unmangled Function Name
- Function Parameter Lists
- Constant Values
- Global Variables
- External Calls
- Local Variable Count
This sequence reflects the relative strength of each feature as a heuristic for identifying a function. Higher-priority features provide more reliable indicators of a function's identity.
-
The analysis stops as soon as a match is found in either the code blocks before or after vulnerability fix from VulSource. For example:
- If a match is found on the Unmangled Function Name, the vulnerability is shortlisted for Dynamic Analysis.
- If not, the engine proceeds to compare Function Parameter Lists, and so on.
4. Dynamic Analysis
Shortlisted vulnerabilities undergo Dynamic Analysis using a sandboxed emulator.
-
The emulator runs pseudo assembly code for:
- The suspected vulnerable code block from the target binary
- The corresponding code blocks before or after vulnerability fix from VulSource
-
It emulates memory and register access, fuzzes function parameters, and logs runtime behavior.
Extracted dynamic features include:
- Function Prototype
- Code Coverage
- Variable Change Logs
- Function Call Logs
- Similarity of Called Functions
Scoring System:
- Significant differences in code coverage reduce the score.
- Variable change logs are compared for similarity; match percentages contribute to the score.
- Average similarity of called functions is added to the score.
5. Result Output
Based on similarity scores between the target binary and vulnerability code blocks ( before or after fix), the engine classifies the vulnerability as:
FixedVulnerableInvulnerable
The final result includes:
- Enriched vulnerability data
- References to pseudo assembly code diffs
- References to source code diffs
1.6.2 External Vulnerability Scanner
When SourceGuard executes a scan and the Project specified an External Vulnerability Scanner, it can
- query the External Vulnerability Scanner for a latest active (not expired) report
- trigger a new scan on External Vulnerability Scanner
- allow user to select a particular report on External Vulnerability Scanner
1. and 2. are applicable for scan on the Project level (manual or scheduled) and it will be a Project Setting.
3. can be triggered in manual scan for an Asset, default is latest. If user wants to select a particular report, SourceGuard will query External Vulnerability Scanner for the reports available and generate Vulnerability Report with the selected external report.
1.6.2.1 Tenable scan template
- scan template can be created and assigned for each Asset (by the template id in Tenable Vulnerability Management system)
- user can create scan template and pass to SourceGuard as default for new Asset
- SourceGuard can use previous scan's template if there is an existing report
1.6.3 Vulnerability Report
The scan report contains a list of vulnerabilities, with these properties:
- Asset ID
- Vulnerability ID
- VulSource
- enriched vulnerability's data scraped in VulSource
If External Vulnerability Scanner is specified for the Project, a report from External Vulnerability Scanner will be merged to the Vulnerability Report based on Vulnerability ID.
Depending on the source of the vulnerability, a Vulnerability will be put in one of these three categories:
- Common Positives
- SourceGuard Only Positives
- External Positives minus External False Positives
- External False Positives
SourceGuard performs vulnerability classification using code from target binaries and patch information from public vulnerability database as ground truth. This enables SourceGuard to identify and classify false positives in reports from external vulnerability scanners as eitherInvulnerableorFixed.
These entries can be de-emphasized in gray to represent the number of vulnerabilities that SourceGuard successfully filters out.